Products
Solar Panels
- On-Grid
- Off-Grid
- Hybrid
On Grid Solar Panels
- Your panels generate power that you consume directly using devices and appliances, all through the day. If your usage is conservative, the excess unused power simply gets fed back into the power grid, adding credits to your electricity bill to offset your payment to the Board.
- At night, when the panels are dormant sans sunlight, you consume power off the grid as always, like any other consumer.
- These systems are ideal for residential properties, community and public buildings, businesses and schools since they offer the security or backup of still being connected to the power grid.
Off Grid Solar Panels
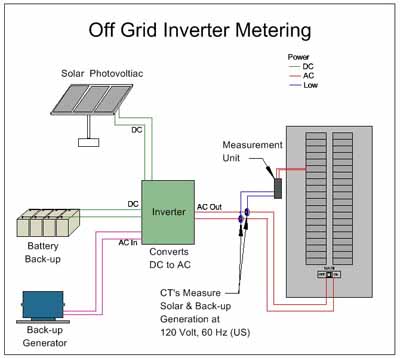
- Off-grid systems work independently of the grid but have batteries which can store the solar power generated by the system. The system usually consists of solar panels, battery, charge controller, grid box, inverter, mounting structure and balance of systems. The panels store enough sunlight during the day and use the excess power generated in the night.
Hybrid Solar Panels
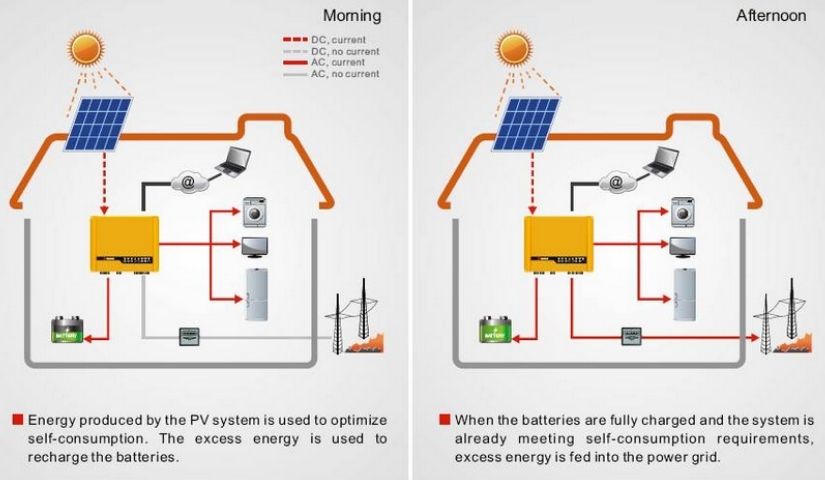
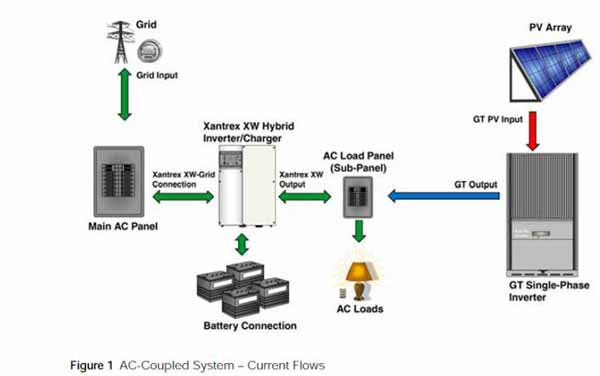
- Hybrid solar systems generate power in the same way as a common grid-tie solar system but use special hybrid inverters and batteries to store energy for later use. This ability to store energy enables most hybrid systems to also operate as a backup power supply during a blackout, similar to a UPS system.
Solar ON Grid / Off Grid Inverters / UPS .All capacities:
Hybrid Solar Inverters
Off Grid Solar Inverters
Grid-Tie Inverters
Solar DC Cables in all Varieties
Types of Wire:
Generally, there are two types of wires in the market, such as
1. AC Wire
2. DC Wire
What are AC & DC Wire?
In our ecosystem, we use two types of appliances, AC Appliances and DC Appliances. AC Appliances work on 230V AC current whereas DC Appliances work on 12V, 24V, and 48V.
So, let’s understand what is the difference between AC Wire & DC Wire?
Now, we come to the main point – A Solar Wire!
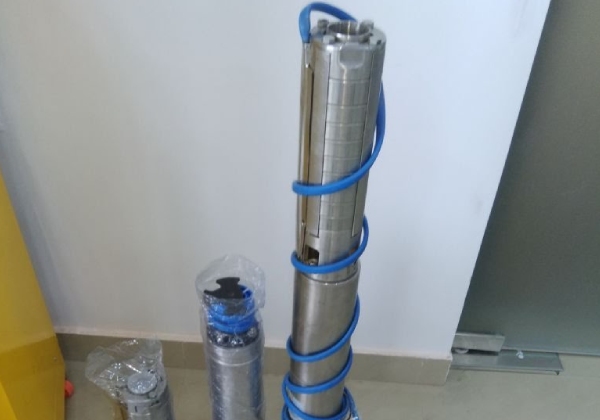
Solar Water A/C and DC Pump Systems
A solar pump uses power derived from sunlight that is converted into electrical power by Solar Photo Voltaic (SPV) modules, which give higher power output in the afternoons and lower power output in the early morning and evening. As a result, solar pump works on varying power input and gives varying water output at a given pump duty head. The most important parameters to select a solar pump are: how much water is needed daily, at what pump duty head, and at which location. The location is important because solar energy varies from region to region, and sizing of solar panels depends on the capacity of solar pumps and also solar radiation of that region.
Solar Lighting Systems
Driven by energy cost, the lighting industry sector has been on an energy-efficiency mission, going back more than half a century to the broad deployment of fluorescent lighting in commercial settings, and gaining in earnest in the 1980s with the development of the compact fluorescent lamp (CFL). Increasingly, however, it’s become clear that minimizing energy usage goes far beyond the light source. Indeed, we have regularly covered controls that can compound savings through occupancy sensing and dimming. The opportunity for better efficiency also extends to the power grid both inside and outside of buildings and to renewable sources such as solar. Let’s discuss how DC-grid technology can deliver significant energy savings, especially when combined with inherently efficient LED sources
The broad topic of DC versus AC grids is beyond our scope here, but if we look inside a commercial building the opportunities for DC distribution become clear (Fig. 1). There are two primary reasons that now may be the time for DC power distribution in buildings. First, we can minimize the number of lossy power conversions with a DC grid. Second, renewable sources such as solar panels produce DC power. And despite the relatively low conversion efficiency of solar panels, they can power efficient LED fixtures.